|
||
|
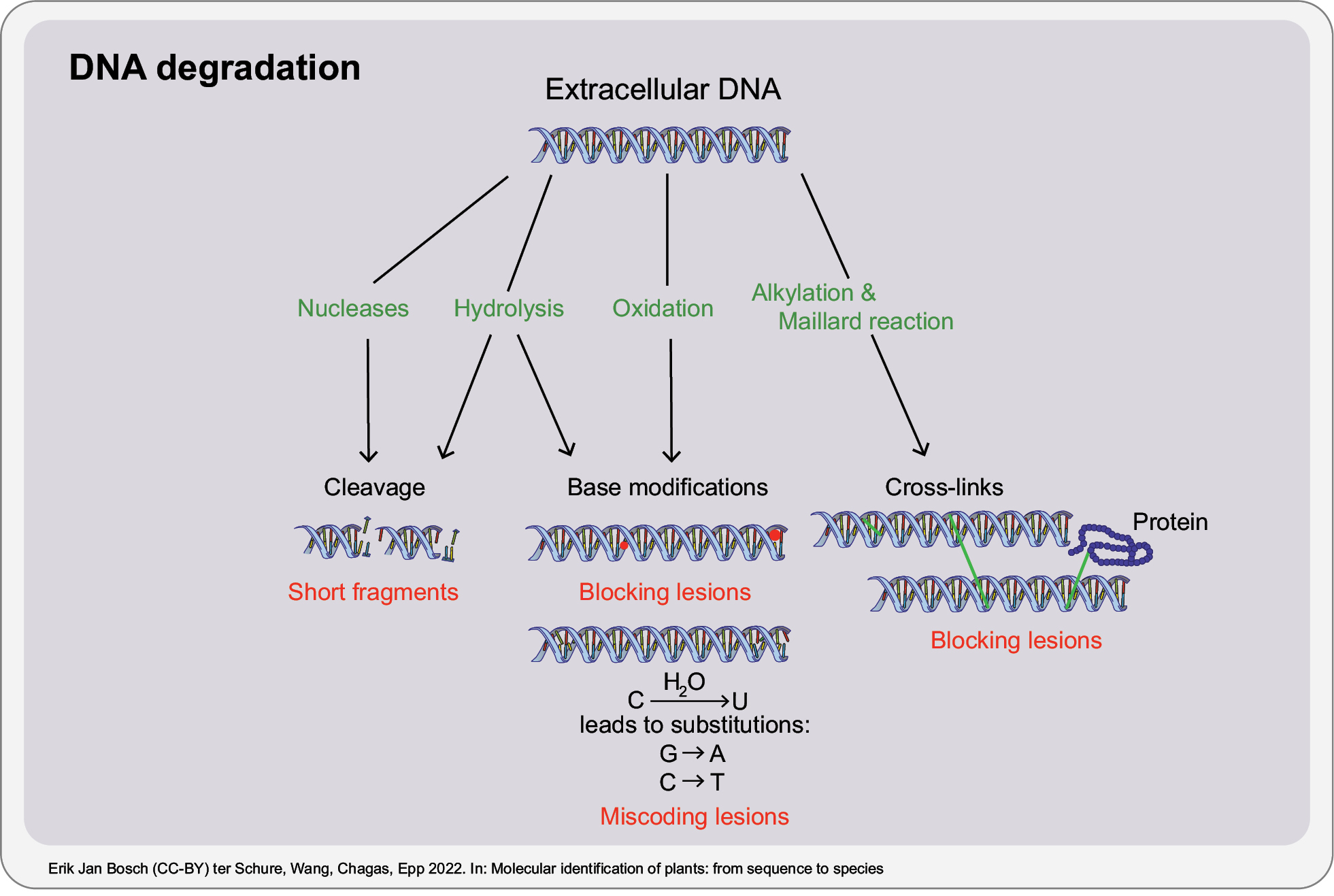
Schematic overview of DNA degradation processes (hydrolysis, oxidation, alkylation and Maillard reaction) that can cause DNA damage in the form of cleavage, base modifications or cross-links. The major mechanism leading to miscoding lesions in aDNA is the hydrolysis of cytosine to uracil, which leads to G to A and C to T substitutions by DNA polymerases, whereas blocking lesions can obstruct the movement of DNA polymerases during PCR (Dabney et al. 2013). |