|
||
|
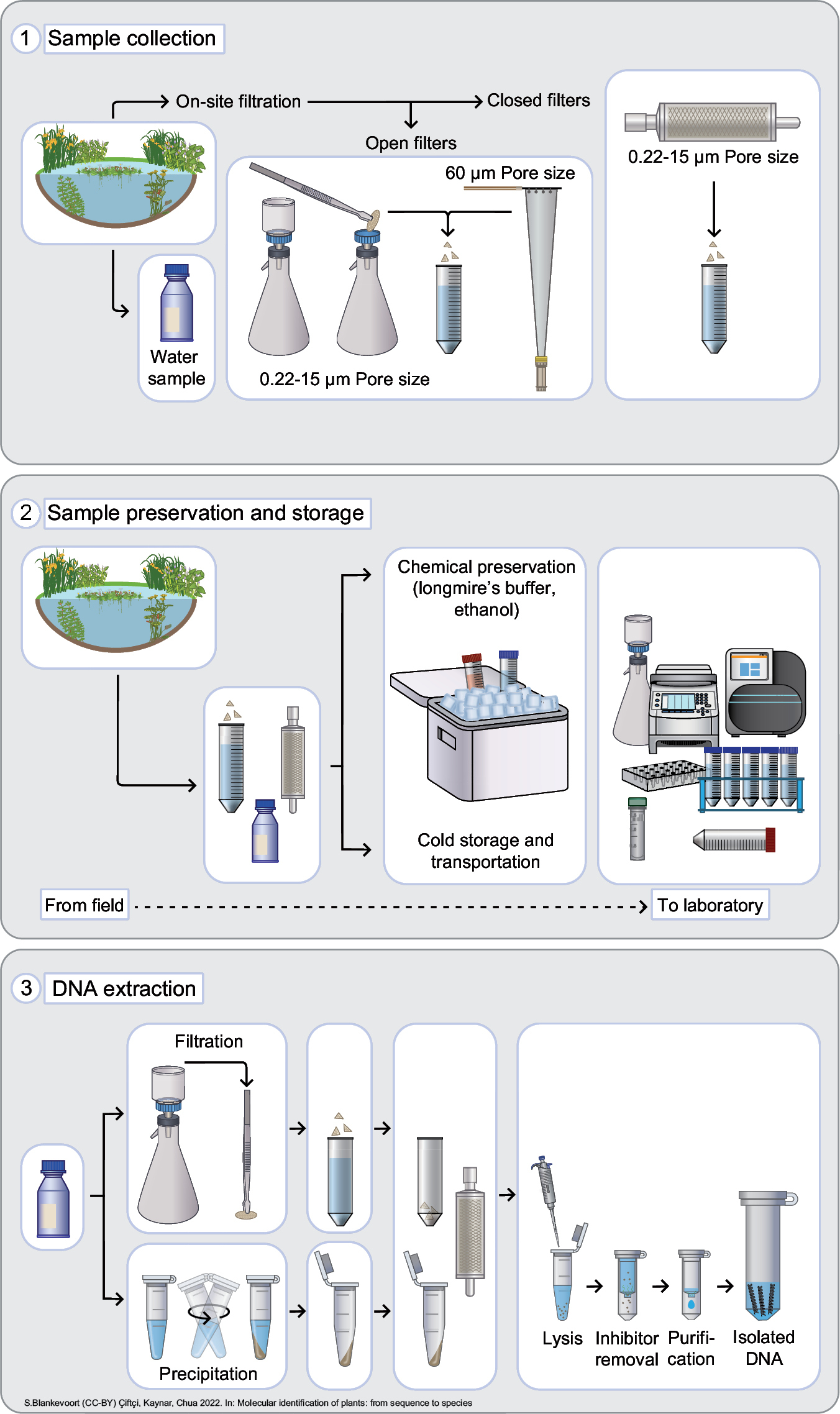
Chapter 3 Infographic: Summary of steps from field collection of water samples to DNA extraction in the laboratory. (1) Open or closed (encapsulated/cartridge) filters can be used for filtering water samples on-site. Large filters (e.g., plankton net with 60 μm pore size) are preferred for filtering larger volumes of water, while small pore size filters can usually process a few litres. Closed filters offer the advantage of preventing contamination, therefore they are more commonly used for on-site filtration. (2) Degradation is another important issue that should be prevented until DNA extraction. Water or filter samples can either be preserved in a chemical buffer or transported in cold and dark conditions to the laboratory for further processing. (3) Plant DNA in water samples can be captured by filtration or precipitation. When using filtration, samples are usually incubated in a lysis solution to extract DNA, while in precipitation samples are mixed with ethanol and DNA is collected in the pellet. Commercial DNA isolation kits specifically designed for environmental sample types are commonly used with some small modifications. |